Array Reverse in C/C++/Java/Python/JavaScript
Last Updated :
17 Apr, 2024
Array reverse or reverse a array means changing the position of each number of the given array to its opposite position from end, i.e. if a number is at position 1 then its new position will be Array.length, similarly if a number is at position 2 then its new position will be Array.length – 1, and so on.
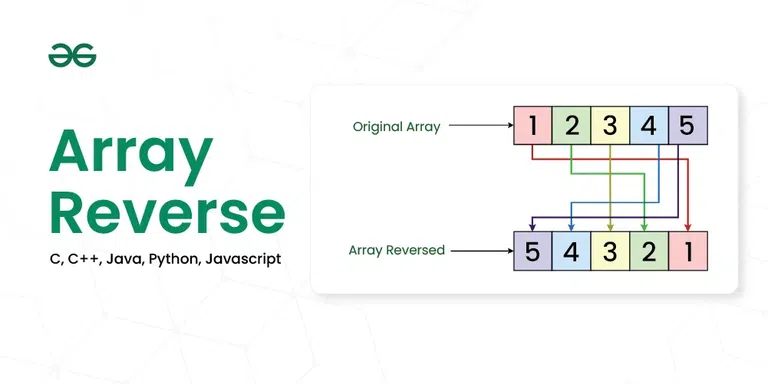
Array Reverse in C/C++/Java/Python/JavaScript
Given an array (or string), the task is to reverse the array/string.
Examples:
Input: original_array[] = {1, 2, 3} Output: array_reversed[] = {3, 2, 1}
Input: original_array[] = {4, 5, 1, 2}
Output: array_reversed[] = {2, 1, 5, 4}
- Create a new array of the same size as the original array.
- Copy elements from the original array to the new array in reverse order.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>;
using namespace std;
void reverseArrayExtraArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int reversedArr[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
reversedArr[i] = arr[size - i - 1];
}
// Print reversed array
cout << "Reversed Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
std::cout << reversedArr[i] << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
int originalArr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int size = sizeof(originalArr) / sizeof(originalArr[0]);
reverseArrayExtraArray(originalArr, size);
}
#include <stdio.h>
void reverseArrayExtraArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int reversedArr[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
reversedArr[i] = arr[size - i - 1];
}
// Print reversed array
printf("Reversed Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", reversedArr[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int originalArr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int size = sizeof(originalArr) / sizeof(originalArr[0]);
reverseArrayExtraArray(originalArr, size);
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
public class ReverseArrayExtraArray {
public static void reverseArrayExtraArray(int[] arr)
{
int[] reversedArr = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
reversedArr[i] = arr[arr.length - i - 1];
}
// Print reversed array
System.out.print("Reversed Array: ");
for (int i : reversedArr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] originalArr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
reverseArrayExtraArray(originalArr);
}
}
def reverse_array_extra_array(arr):
reversed_arr = arr[::-1]
# Print reversed array
print("Reversed Array:", end=" ")
for i in reversed_arr:
print(i, end=" ")
# Example usage:
original_arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
reverse_array_extra_array(original_arr)
using System;
class Program {
static void ReverseArrayExtraArray(int[] arr) {
int[] reversedArr = new int[arr.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
reversedArr[i] = arr[arr.Length - i - 1];
}
// Print reversed array
Console.Write("Reversed Array: ");
foreach (int num in reversedArr) {
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
}
static void Main() {
int[] originalArr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
ReverseArrayExtraArray(originalArr);
}
}
function reverseArrayExtraArray(arr) {
const reversedArr = arr.slice().reverse();
// Print reversed array
process.stdout.write("Reversed Array: ");
reversedArr.forEach(element => process.stdout.write(element + " "));
}
// Example usage:
const originalArr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
reverseArrayExtraArray(originalArr);
OutputReversed Array: 5 4 3 2 1
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Copying elements to a new array is a linear operation.
- Auxiliary Space Complexity: O(n)
- Additional space is used to store the new array.
2. Array Reverse Using a Loop (In-place):
- Iterate through the array using two pointers (start and end).
- Swap elements at the start and end pointers.
- Move the start pointer towards the end and the end pointer towards the start until they meet or cross each other.
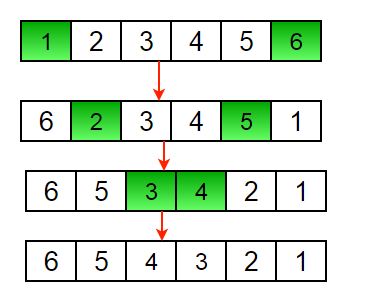
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C++
// Iterative C++ program to reverse an array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>;
using namespace std;
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
while (start < end) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
/* Utility function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// To print original array
printArray(arr, n);
// Function calling
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
cout << "Reversed array is" << endl;
// To print the Reversed array
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// Iterative C program to reverse an array
#include <stdio.h>
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
int temp;
while (start < end) {
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printArray(arr, n);
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("Reversed array is \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
public class GFG {
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
static void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end) {
int temp;
while (start < end) {
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
static void printArray(int arr[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
printArray(arr, 6);
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
System.out.print("Reversed array is \n");
printArray(arr, 6);
}
}
# Iterative python program to reverse an array
# Function to reverse A[] from start to end
def reverseList(A, start, end):
while start < end:
A[start], A[end] = A[end], A[start]
start += 1
end -= 1
# Driver function to test above function
A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print(A)
reverseList(A, 0, 5)
print("Reversed list is")
print(A)
# This program is contributed by Pratik Chhajer
// Iterative C# program to reverse an
// array
using System;
class GFG {
/* Function to reverse arr[] from
start to end*/
static void reverseArray(int[] arr, int start, int end)
{
int temp;
while (start < end) {
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
/* Utility that prints out an
array on a line */
static void printArray(int[] arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
printArray(arr, 6);
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
Console.Write("Reversed array is \n");
printArray(arr, 6);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
// Iterative Javascript program to reverse an array
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
function reverseArray(arr,start,end)
{
while (start < end)
{
var temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
/* Utility function to print an array */
function printArray(arr,size)
{
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++){
console.log(arr[i]);
}
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
var arr= [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
var n = 6;
// To print original array
printArray(arr, n);
// Function calling
reverseArray(arr, 0, n-1);
console.log("Reversed array is");
printArray(arr, n);
<?php
// Iterative PHP program
// to reverse an array
/* Function to reverse
$arr from start to end*/
function reverseArray(&$arr, $start, $end)
{
while ($start < $end)
{
$temp = $arr[$start];
$arr[$start] = $arr[$end];
$arr[$end] = $temp;
$start++;
$end--;
}
}
/* Utility function to
print an array */
function printArray(&$arr, $size)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
echo "\n";
}
// Driver code
$arr = array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// To print original array
printArray($arr, 6);
// Function calling
reverseArray($arr, 0, 5);
echo "Reversed array is" ."\n";
// To print the Reversed array
printArray($arr, 6);
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
?>
Output1 2 3 4 5 6
Reversed array is
6 5 4 3 2 1
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- The loop runs through half of the array, so it’s linear with respect to the array size.
- Auxiliary Space Complexity: O(1)
- In-place reversal, meaning it doesn’t use additional space.
3. Array Reverse Inbuilt Methods (Non In-place):
- Use inbuilt methods like
reverse in Python or Array.Reverse in C#.
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C++
#include <algorithm> // for std::reverse
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int originalArray[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int length
= sizeof(originalArray) / sizeof(originalArray[0]);
// Using inbuilt method in C++
std::reverse(originalArray, originalArray + length);
// Print the reversed array
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
std::cout << originalArray[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayReverse {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] originalArray = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Using inbuilt method in Java
int[] reversedArray = new int[originalArray.length];
for (int i = 0; i < originalArray.length; i++) {
reversedArray[i]
= originalArray[originalArray.length - 1
- i];
}
// Print the reversed array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(reversedArray));
}
}
original_array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Using inbuilt method in Python
reversed_array = list(reversed(original_array))
# Print the reversed array
print(reversed_array)
using System;
class Program {
static void Main()
{
int[] originalArray = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Using inbuilt method in C#
Array.Reverse(originalArray);
// Print the reversed array
foreach(int num in originalArray)
{
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
}
}
let originalArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Using inbuilt method in JavaScript
let reversedArray = originalArray.slice().reverse();
// Print the reversed array
console.log(reversedArray);
- Time Complexity: O(n) The
reverse method typically has linear time complexity. - Auxiliary Space Complexity: O(n)
- Additional space is used to store the reversed array.
4. Array Reverse Recursion (In-place or Non In-place):
- Define a recursive function that takes an array as input.
- Swap the first and last elements.
- Recursively call the function with the remaining subarray.
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C++
// Recursive C++ program to reverse an array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>;
using namespace std;
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
if (start >= end)
return;
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
// Recursive Function calling
reverseArray(arr, start + 1, end - 1);
}
/* Utility function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
// To print original array
printArray(arr, 6);
// Function calling
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
cout << "Reversed array is" << endl;
// To print the Reversed array
printArray(arr, 6);
return 0;
}
// Recursive C program to reverse an array
#include <stdio.h>;
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
int temp;
if (start >= end)
return;
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
reverseArray(arr, start + 1, end - 1);
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
printArray(arr, 6);
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
printf("Reversed array is \n");
printArray(arr, 6);
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class ReverseArray {
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
static void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end)
{
int temp;
if (start >= end)
return;
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
reverseArray(arr, start + 1, end - 1);
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
static void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println("");
}
/*Driver function to check for above functions*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
printArray(arr, 6);
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
System.out.println("Reversed array is ");
printArray(arr, 6);
}
}
/*This article is contributed by Devesh Agrawal*/
# Recursive python program to reverse an array
# Function to reverse A[] from start to end
def reverseList(A, start, end):
if start >= end:
return
A[start], A[end] = A[end], A[start]
reverseList(A, start+1, end-1)
# Driver function to test above function
A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print(A)
reverseList(A, 0, 5)
print("Reversed list is")
print(A)
# This program is contributed by Pratik Chhajer
// C# program to reverse an array
using System;
class GFG {
/* Function to reverse arr[]
from start to end*/
static void reverseArray(int[] arr, int start, int end)
{
int temp;
if (start >= end)
return;
temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
reverseArray(arr, start + 1, end - 1);
}
/* Utility that prints out an
array on a line */
static void printArray(int[] arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine("");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
printArray(arr, 6);
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
Console.WriteLine("Reversed array is ");
printArray(arr, 6);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
// Recursive Javascript program to reverse an array
/* Function to reverse arr[] from start to end*/
function reverseArray(arr,start,end)
{
var temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
// Recursive Function calling
if (start+1<end-1){
reverseArray(arr, start + 1, end - 1);
}
}
/* Utility function to print an array */
function printArray(arr,size)
{
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++){
console.log(arr[i]);
}
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
var arr= [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
// To print original array
printArray(arr, 6);
// Function calling
reverseArray(arr, 0, 5);
console.log("Reversed array is");
// To print the Reversed array
printArray(arr, 6);
<?php
// Recursive PHP program to reverse an array
/* Function to reverse $arr[] from $start to $end */
function reverseArray(&$arr, $start, $end)
{
if ($start >= $end) {
return;
}
$temp = $arr[$start];
$arr[$start] = $arr[$end];
$arr[$end] = $temp;
// Recursive Function calling
reverseArray($arr, $start + 1, $end - 1);
}
/* Utility function to print an array */
function printArray(&$arr, $size)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++) {
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
}
echo "\n";
}
// Driver function to test above functions
$arr = array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// To print original array
printArray($arr, 6);
// Function calling
reverseArray($arr, 0, 5);
echo "Reversed array is" . "\n";
// To print the Reversed array
printArray($arr, 6);
?>
Output1 2 3 4 5 6
Reversed array is
6 5 4 3 2 1
- Time Complexity: O(n). The recursion goes through each element once, so it’s linear.
- Auxiliary Space Complexity: O(n) for non in-place, O(log n) for in-place (due to recursion stack).
5. Array Reverse Stack (Non In-place):
- Push each element of the array onto a stack.
- Pop elements from the stack to form the reversed array.
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C++
#include <iostream>;
#include <stack>;
#include <vector>;
void reverseArrayUsingStack(int arr[], int size)
{
std::stack<int> stack;
// Push elements onto the stack
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
stack.push(arr[i]);
}
// Pop elements from the stack to reverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = stack.top();
stack.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
reverseArrayUsingStack(arr, size);
std::cout << "Reversed Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
std::cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>;
#include <stdlib.h>;
#define MAX_SIZE 100
struct Stack {
int arr[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
};
void push(struct Stack* stack, int element)
{
if (stack->top == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("Stack Overflow\n");
return;
}
stack->arr[++stack->top] = element;
}
int pop(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (stack->top == -1) {
printf("Stack Underflow\n");
exit(1);
}
return stack->arr[stack->top--];
}
void reverseArrayUsingStack(int arr[], int size)
{
struct Stack stack;
stack.top = -1;
// Push elements onto the stack
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
push(&stack, arr[i]);
}
// Pop elements from the stack to reverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = pop(&stack);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
reverseArrayUsingStack(arr, size);
printf("Reversed Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReverseArrayUsingStack {
public static void reverseArrayUsingStack(int[] arr)
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// Push elements onto the stack
for (int element : arr) {
stack.push(element);
}
// Pop elements from the stack to reverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
reverseArrayUsingStack(arr);
System.out.print("Reversed Array: ");
for (int element : arr) {
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
}
}
def reverse_array_using_stack(arr):
stack = []
# Push elements onto the stack
for element in arr:
stack.append(element)
# Pop elements from the stack to reverse the array
for i in range(len(arr)):
arr[i] = stack.pop()
# Example usage:
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
reverse_array_using_stack(arr)
print("Reversed Array:", arr)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program {
static void ReverseArrayUsingStack(int[] arr)
{
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
// Push elements onto the stack
foreach(int element in arr) { stack.Push(element); }
// Pop elements from the stack to reverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
arr[i] = stack.Pop();
}
}
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
ReverseArrayUsingStack(arr);
Console.Write("Reversed Array: ");
foreach(int element in arr)
{
Console.Write(element + " ");
}
}
}
function reverseArrayUsingStack(arr) {
let stack = [];
// Push elements onto the stack
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
stack.push(arr[i]);
}
// Pop elements from the stack to reverse the array
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = stack.pop();
}
}
// Example usage:
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
reverseArrayUsingStack(arr);
console.log("Reversed Array:", arr);
OutputReversed Array: 5 4 3 2 1
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Pushing and popping each element onto/from the stack requires linear time.
- Auxiliary Space Complexity: O(n)
- Additional space is used to store the stack.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...