Subset Sum Problem
Last Updated :
07 Nov, 2023
Given a set of non-negative integers and a value sum, the task is to check if there is a subset of the given set whose sum is equal to the given sum.
Examples:
Input: set[] = {3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2}, sum = 9
Output: True
Explanation: There is a subset (4, 5) with sum 9.
Input: set[] = {3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2}, sum = 30
Output: False
Explanation: There is no subset that add up to 30.
Subset Sum Problem using Recursion:
For the recursive approach, there will be two cases.
- Consider the ‘last’ element to be a part of the subset. Now the new required sum = required sum – value of ‘last’ element.
- Don’t include the ‘last’ element in the subset. Then the new required sum = old required sum.
In both cases, the number of available elements decreases by 1.
Mathematically the recurrence relation will look like the following:
isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) = isSubsetSum(set, n-1, sum) | isSubsetSum(set, n-1, sum-set[n-1])
Base Cases:
isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) = false, if sum > 0 and n = 0
isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) = true, if sum = 0
The structure of the recursion tree will be like the following:
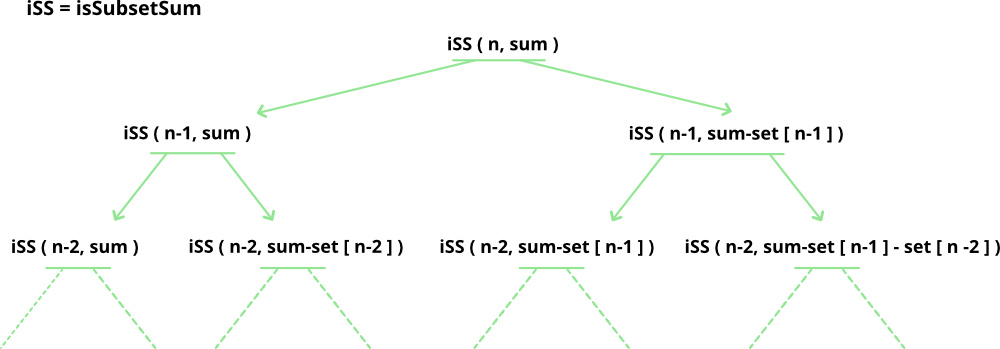
Structure of the recursion tree of the above recursion formula
Follow the below steps to implement the recursion:
- Build a recursive function and pass the index to be considered (here gradually moving from the last end) and the remaining sum amount.
- For each index check the base cases and utilize the above recursive call.
- If the answer is true for any recursion call, then there exists such a subset. Otherwise, no such subset exists.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0)
return false;
if (set[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum - set[n - 1]);
}
int main()
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = sizeof(set) / sizeof(set[0]);
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
cout << "Found a subset with given sum";
else
cout << "No subset with given sum";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
bool isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0)
return false;
if (set[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum - set[n - 1]);
}
int main()
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = sizeof(set) / sizeof(set[0]);
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
printf("Found a subset with given sum");
else
printf("No subset with given sum");
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static boolean isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0)
return false;
if (set[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum - set[n - 1]);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = set.length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
System.out.println("Found a subset"
+ " with given sum");
else
System.out.println("No subset with"
+ " given sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubsetSum(set, n, sum):
if (sum == 0):
return True
if (n == 0):
return False
if (set[n - 1] > sum):
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum)
return isSubsetSum(
set, n-1, sum) or isSubsetSum(
set, n-1, sum-set[n-1])
if __name__ == '__main__':
set = [3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2]
sum = 9
n = len(set)
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == True):
print("Found a subset with given sum")
else:
print("No subset with given sum")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static bool isSubsetSum(int[] set, int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0)
return false;
if (set[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum - set[n - 1]);
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] set = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = set.Length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
Console.WriteLine(
"Found a subset with given sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("No subset with given sum");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isSubsetSum(set, n, sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0)
return false;
if (set[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(set, n - 1, sum - set[n - 1]);
}
let set = [ 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 ];
let sum = 9;
let n = set.length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
document.write("Found a subset with given sum");
else
document.write("No subset with given sum");
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function isSubsetSum($set, $n, $sum)
{
if ($sum == 0)
return true;
if ($n == 0)
return false;
if ($set[$n - 1] > $sum)
return isSubsetSum($set, $n - 1, $sum);
return isSubsetSum($set, $n - 1, $sum) ||
isSubsetSum($set, $n - 1,
$sum - $set[$n - 1]);
}
$set = array(3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2);
$sum = 9;
$n = 6;
if (isSubsetSum($set, $n, $sum) == true)
echo"Found a subset with given sum";
else
echo "No subset with given sum";
?>
|
Output
Found a subset with given sum
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(2n) The above solution may try all subsets of the given set in worst case. Therefore time complexity of the above solution is exponential. The problem is in-fact NP-Complete (There is no known polynomial time solution for this problem).
- Auxiliary Space: O(n) where n is recursion stack space.
Subset Sum Problem using Memoization:
As seen in the previous recursion method, each state of the solution can be uniquely identified using two variables – the index and the remaining sum. So create a 2D array to store the value of each state to avoid recalculation of the same state.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tab[2000][2000];
int subsetSum(int a[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return 1;
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
if (tab[n - 1][sum] != -1)
return tab[n - 1][sum];
if (a[n - 1] > sum)
return tab[n - 1][sum] = subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum);
else
{
return tab[n - 1][sum] = subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum) ||
subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum - a[n - 1]);
}
}
int main()
{
memset(tab, -1, sizeof(tab));
int n = 5;
int a[] = {1, 5, 3, 7, 4};
int sum = 12;
if (subsetSum(a, n, sum))
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int subsetSum(int a[], int n, int sum)
{
int tab[][] = new int[n + 1][sum + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
tab[i][j] = -1;
}
}
if (sum == 0)
return 1;
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
if (tab[n - 1][sum] != -1)
return tab[n - 1][sum];
if (a[n - 1] > sum)
return tab[n - 1][sum]
= subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum);
else {
if (subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum) != 0
|| subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum - a[n - 1])
!= 0) {
return tab[n - 1][sum] = 1;
}
else
return tab[n - 1][sum] = 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int a[] = { 1, 5, 3, 7, 4 };
int sum = 12;
if (subsetSum(a, n, sum) != 0) {
System.out.println("YES\n");
}
else
System.out.println("NO\n");
}
}
|
Python3
tab = [[-1 for i in range(2000)] for j in range(2000)]
def subsetSum(a, n, sum):
if (sum == 0):
return 1
if (n <= 0):
return 0
if (tab[n - 1][sum] != -1):
return tab[n - 1][sum]
if (a[n - 1] > sum):
tab[n - 1][sum] = subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum)
return tab[n - 1][sum]
else:
tab[n - 1][sum] = subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum)
return tab[n - 1][sum] or subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum - a[n - 1])
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 5
a = [1, 5, 3, 7, 4]
sum = 12
if (subsetSum(a, n, sum)):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int subsetSum(int []a, int n, int sum)
{
int [,]tab = new int[n + 1,sum + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
tab[i,j] = -1;
}
}
if (sum == 0)
return 1;
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
if (tab[n - 1,sum] != -1)
return tab[n - 1,sum];
if (a[n - 1] > sum)
return tab[n - 1,sum]
= subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum);
else {
if (subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum) != 0
|| subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum - a[n - 1])
!= 0) {
return tab[n - 1,sum] = 1;
}
else
return tab[n - 1,sum] = 0;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int []a = { 1, 5, 3, 7, 4 };
int sum = 12;
if (subsetSum(a, n, sum) != 0) {
Console.Write("YES\n");
}
else
Console.Write("NO\n");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function subsetSum(a, n, sum) {
if (sum == 0)
return 1;
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
if (tab[n - 1][sum] != -1)
return tab[n - 1][sum];
if (a[n - 1] > sum)
return tab[n - 1][sum] = subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum);
else {
return tab[n - 1][sum] = subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum) ||
subsetSum(a, n - 1, sum - a[n - 1]);
}
}
let tab = Array(2000).fill().map(() => Array(2000).fill(-1));
let n = 5;
let a = [1, 5, 3, 7, 4];
let sum = 12;
if (subsetSum(a, n, sum)) {
document.write("YES" + "<br>");
}
else {
document.write("NO" + "<br>");
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(sum*n), where sum is the ‘target sum’ and ‘n’ is the size of array.
- Auxiliary Space: O(sum*n) + O(n) -> O(sum*n) = the size of 2-D array is sum*n and O(n)=auxiliary stack space.
To solve the problem in Pseudo-polynomial time we can use the Dynamic programming approach.
So we will create a 2D array of size (n + 1) * (sum + 1) of type boolean. The state dp[i][j] will be true if there exists a subset of elements from set[0 . . . i] with sum value = ‘j’.
The dynamic programming relation is as follows:
if (A[i-1] > j)
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] OR dp[i-1][j-set[i-1]]
This means that if the current element has a value greater than the ‘current sum value’ we will copy the answer for previous cases and if the current sum value is greater than the ‘ith’ element we will see if any of the previous states have already experienced the sum= j OR any previous states experienced a value ‘j – set[i]’ which will solve our purpose.
Illustration:
See the below illustration for a better understanding:
Consider set[] = {3, 4, 5, 2} and sum = 6.
The table will look like the following where the column number represents the sum and the row number represents the index of set[]:
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
F
|
F
|
F
|
F
|
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
F
|
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
T
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
|
T
|
F
|
F
|
T
|
T
|
T
|
F
|
|
T
|
F
|
T
|
T
|
T
|
T
|
T
|
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
bool subset[n + 1][sum + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
subset[i][0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
subset[0][i] = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
if (j < set[i - 1])
subset[i][j] = subset[i - 1][j];
if (j >= set[i - 1])
subset[i][j]
= subset[i - 1][j]
|| subset[i - 1][j - set[i - 1]];
}
}
return subset[n][sum];
}
int main()
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = sizeof(set) / sizeof(set[0]);
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
cout << "Found a subset with given sum";
else
cout << "No subset with given sum";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
bool isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
bool subset[n + 1][sum + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
subset[i][0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
subset[0][i] = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
if (j < set[i - 1])
subset[i][j] = subset[i - 1][j];
if (j >= set[i - 1])
subset[i][j]
= subset[i - 1][j]
|| subset[i - 1][j - set[i - 1]];
}
}
return subset[n][sum];
}
int main()
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = sizeof(set) / sizeof(set[0]);
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
printf("Found a subset with given sum");
else
printf("No subset with given sum");
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static boolean isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
boolean subset[][] = new boolean[sum + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
subset[0][i] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
subset[i][0] = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
subset[i][j] = subset[i][j - 1];
if (i >= set[j - 1])
subset[i][j]
= subset[i][j]
|| subset[i - set[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
return subset[sum][n];
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = set.length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
System.out.println("Found a subset"
+ " with given sum");
else
System.out.println("No subset with"
+ " given sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubsetSum(set, n, sum):
subset = ([[False for i in range(sum + 1)]
for i in range(n + 1)])
for i in range(n + 1):
subset[i][0] = True
for i in range(1, sum + 1):
subset[0][i] = False
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, sum + 1):
if j < set[i-1]:
subset[i][j] = subset[i-1][j]
if j >= set[i-1]:
subset[i][j] = (subset[i-1][j] or
subset[i - 1][j-set[i-1]])
return subset[n][sum]
if __name__ == '__main__':
set = [3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2]
sum = 9
n = len(set)
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == True):
print("Found a subset with given sum")
else:
print("No subset with given sum")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static bool isSubsetSum(int[] set, int n, int sum)
{
bool[, ] subset = new bool[sum + 1, n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
subset[0, i] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
subset[i, 0] = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
subset[i, j] = subset[i, j - 1];
if (i >= set[j - 1])
subset[i, j]
= subset[i, j]
|| subset[i - set[j - 1], j - 1];
}
}
return subset[sum, n];
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] set = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = set.Length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
Console.WriteLine(
"Found a subset with given sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("No subset with given sum");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isSubsetSum(set, n, sum)
{
let subset = new Array(sum + 1);
for(let i = 0; i < sum + 1; i++)
{
subset[i] = new Array(sum + 1);
for(let j = 0; j < n + 1; j++)
{
subset[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++)
subset[0][i] = true;
for (let i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
subset[i][0] = false;
for (let i = 1; i <= sum; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
subset[i][j] = subset[i][j - 1];
if (i >= set[j - 1])
subset[i][j] = subset[i][j]
|| subset[i - set[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
return subset[sum][n];
}
let set = [ 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 ];
let sum = 9;
let n = set.length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
document.write("Found a subset" + " with given sum");
else
document.write("No subset with" + " given sum");
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function isSubsetSum( $set, $n, $sum)
{
$subset = array(array());
for ( $i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++)
$subset[$i][0] = true;
for ( $i = 1; $i <= $sum; $i++)
$subset[0][$i] = false;
for ($i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
for ($j = 1; $j <= $sum; $j++)
{
if($j < $set[$i-1])
$subset[$i][$j] =
$subset[$i-1][$j];
if ($j >= $set[$i-1])
$subset[$i][$j] =
$subset[$i-1][$j] ||
$subset[$i - 1][$j -
$set[$i-1]];
}
}
return $subset[$n][$sum];
}
$set = array(3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2);
$sum = 9;
$n = count($set);
if (isSubsetSum($set, $n, $sum) == true)
echo "Found a subset with given sum";
else
echo "No subset with given sum";
?>
|
Output
Found a subset with given sum
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(sum * n), where n is the size of the array.
- Auxiliary Space: O(sum*n), as the size of the 2-D array is sum*n.
Subset Sum Problem using Dynamic Programming with space optimization to linear:
Idea:
In previous approach of dynamic programming we have derive the relation between states as given below:
if (A[i-1] > j)
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] OR dp[i-1][j-set[i-1]]
If we observe that for calculating current dp[i][j] state we only need previous row dp[i-1][j] or dp[i-1][j-set[i-1]].
There is no need to store all the previous states just one previous state is used to compute result.
Approach:
- Define two arrays prev and curr of size Sum+1 to store the just previous row result and current row result respectively.
- Once curr array is calculated then curr becomes our prev for the next row.
- When all rows are processed the answer is stored in prev array.
Implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubsetSum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
vector<bool> prev(sum + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
prev[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
prev[i] = false;
vector<bool> curr(sum + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
if (j < set[i - 1])
curr[j] = prev[j];
if (j >= set[i - 1])
curr[j] = prev[j] || prev[j - set[i - 1]];
}
prev = curr;
}
return prev[sum];
}
int main()
{
int set[] = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = sizeof(set) / sizeof(set[0]);
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) == true)
cout << "Found a subset with given sum";
else
cout << "No subset with given sum";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SubsetSum {
static boolean isSubsetSum(int[] set, int n, int sum) {
boolean[] prev = new boolean[sum + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
prev[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
prev[i] = false;
boolean[] curr = new boolean[sum + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
if (j < set[i - 1])
curr[j] = prev[j];
if (j >= set[i - 1])
curr[j] = prev[j] || prev[j - set[i - 1]];
}
prev = Arrays.copyOf(curr, curr.length);
}
return prev[sum];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] set = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = set.length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum))
System.out.println("Found a subset with the given sum");
else
System.out.println("No subset with the given sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubsetSum(nums, n, sum):
prev = [False] * (sum + 1)
prev[0] = True
for i in range(1, n + 1):
curr = [False] * (sum + 1)
for j in range(1, sum + 1):
if j < nums[i - 1]:
curr[j] = prev[j]
if j >= nums[i - 1]:
curr[j] = prev[j] or prev[j - nums[i - 1]]
prev = curr
return prev[sum]
if __name__ == "__main__":
nums = [3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2]
sum_value = 9
n = len(nums)
if isSubsetSum(nums, n, sum_value):
print("Found a subset with the given sum")
else:
print("No subset with the given sum")
|
C#
using System;
class Program
{
static bool IsSubsetSum(int[] set, int n, int sum)
{
bool[,] dp = new bool[n + 1, sum + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i, 0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
dp[0, i] = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++)
{
if (j < set[i - 1])
dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j];
if (j >= set[i - 1])
dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j] || dp[i - 1, j - set[i - 1]];
}
}
return dp[n, sum];
}
static void Main()
{
int[] set = { 3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2 };
int sum = 9;
int n = set.Length;
if (IsSubsetSum(set, n, sum))
Console.WriteLine("Found a subset with given sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("No subset with given sum");
}
}
|
Javascript
function isSubsetSum(set, n, sum) {
let prev = new Array(sum + 1).fill(false);
prev[0] = true;
let curr = [...prev];
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
if (j < set[i - 1]) {
curr[j] = prev[j];
}
if (j >= set[i - 1]) {
curr[j] = prev[j] || prev[j - set[i - 1]];
}
}
prev = [...curr];
}
return prev[sum];
}
let set = [3, 34, 4, 12, 5, 2];
let sum = 9;
let n = set.length;
if (isSubsetSum(set, n, sum)) {
console.log("Found a subset with given sum");
} else {
console.log("No subset with given sum");
}
|
Output
Found a subset with given sum
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(sum * n), where n is the size of the array.
- Auxiliary Space: O(sum), as the size of the 1-D array is sum+1.
Related Articles:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...