In this post, we will look into insertion operation in an Array, i.e., how to insert into an Array, such as:
- Inserting Elements in an Array at the End
- Inserting Elements in an Array at any Position in the Middle
- Inserting Elements in a Sorted Array
1. Inserting Elements in an Array at the End:
In an unsorted array, the insert operation is faster as compared to a sorted array because we don’t have to care about the position at which the element is to be placed.
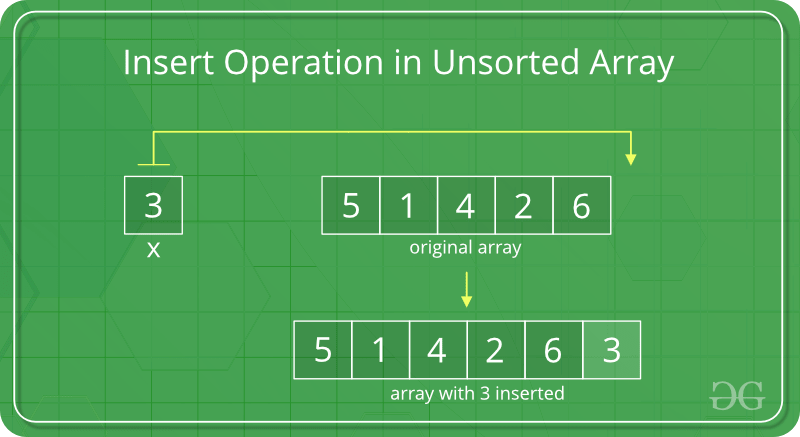
Coding implementation of inserting an element at the end:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// Include the C++ input/output library
using namespace std;
//Using the standard namespace for convenience
// Function to insert a key into an array
int insertSorted(int arr[], int n, int key, int capacity) {
// Check if the array is already full
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
// Add the key at the end of the array
arr[n] = key;
// Return the updated size of the array
return (n + 1);
}
int main() {
int arr[20] = {12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70};
int capacity = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
cout << "\n Before Insertion: ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " "; // Inserting the key into the array
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
cout << "\n After Insertion: ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
//This code is contributed by Dhruv kumar
}
// C program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
#include <stdio.h>
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given capacity.
// n is current size of arr[]. This
// function returns n + 1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
int insertSorted(int arr[], int n, int key, int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is
// already more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[20] = { 12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70 };
int capacity = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
printf("\n Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
// Inserting key
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
printf("\n After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
// Java program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
class Main {
// Function to insert a given key in
// the array. This function returns n+1
// if insertion is successful, else n.
static int insertSorted(int arr[], int n, int key,
int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n
// is already more than or equal to
// capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
int capacity = 20;
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
System.out.print("Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
// Inserting key
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
System.out.print("\n After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
# Python program for inserting
# an element in an unsorted array
# method to insert element
def insert(arr, element):
arr.append(element)
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# declaring array and key to insert
arr = [12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70]
key = 26
# array before inserting an element
print("Before Inserting: ")
print(arr)
# array after Inserting element
insert(arr, key)
print("After Inserting: ")
print(arr)
# Thanks to Aditi Sharma for contributing
# this code
// C# program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
using System;
class main {
// Function to insert a given
// key in the array. This
// function returns n + 1
// if insertion is successful,
// else n.
static int insertSorted(int[] arr, int n, int key,
int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements
// if n is already more than
// or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
int capacity = 20;
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
Console.Write("Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
// Inserting key
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
Console.Write("After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
// Javascript program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
// Function to insert a given
// key in the array. This
// function returns n + 1
// if insertion is successful,
// else n.
function insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements
// if n is already more than
// or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
arr[n] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
let arr = new Array(20);
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
let capacity = 20;
let n = 6;
let i, key = 26;
document.write("Before Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
console.log(arr[i]+" ");
console.log("</br>");
// Inserting key
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
document.write("After Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
console.log(arr[i]+" ");
<?php
// PHP program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given
// capacity. n is current size of arr[].
// This function returns n + 1 if
// insertion is successful, else n.
function insertSorted(&$arr, $n, $key,
$capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is
// already more than or equal to capacity
if ($n >= $capacity)
return $n;
array_push($arr, $key);
return ($n + 1);
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70);
$capacity = 20;
$n = 6;
$key = 26;
echo "Before Insertion: ";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
// Inserting key
$n = insertSorted($arr, $n,
$key, $capacity);
echo "\nAfter Insertion: ";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
// This code is contributed by
// Rajput-Ji
?>
Output
Before Insertion: 12 16 20 40 50 70 After Insertion: 12 16 20 40 50 70 26
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
2. Inserting Elements in an Array at any Position:
Insert operation in an array at any position can be performed by shifting elements to the right, which are on the right side of the required position
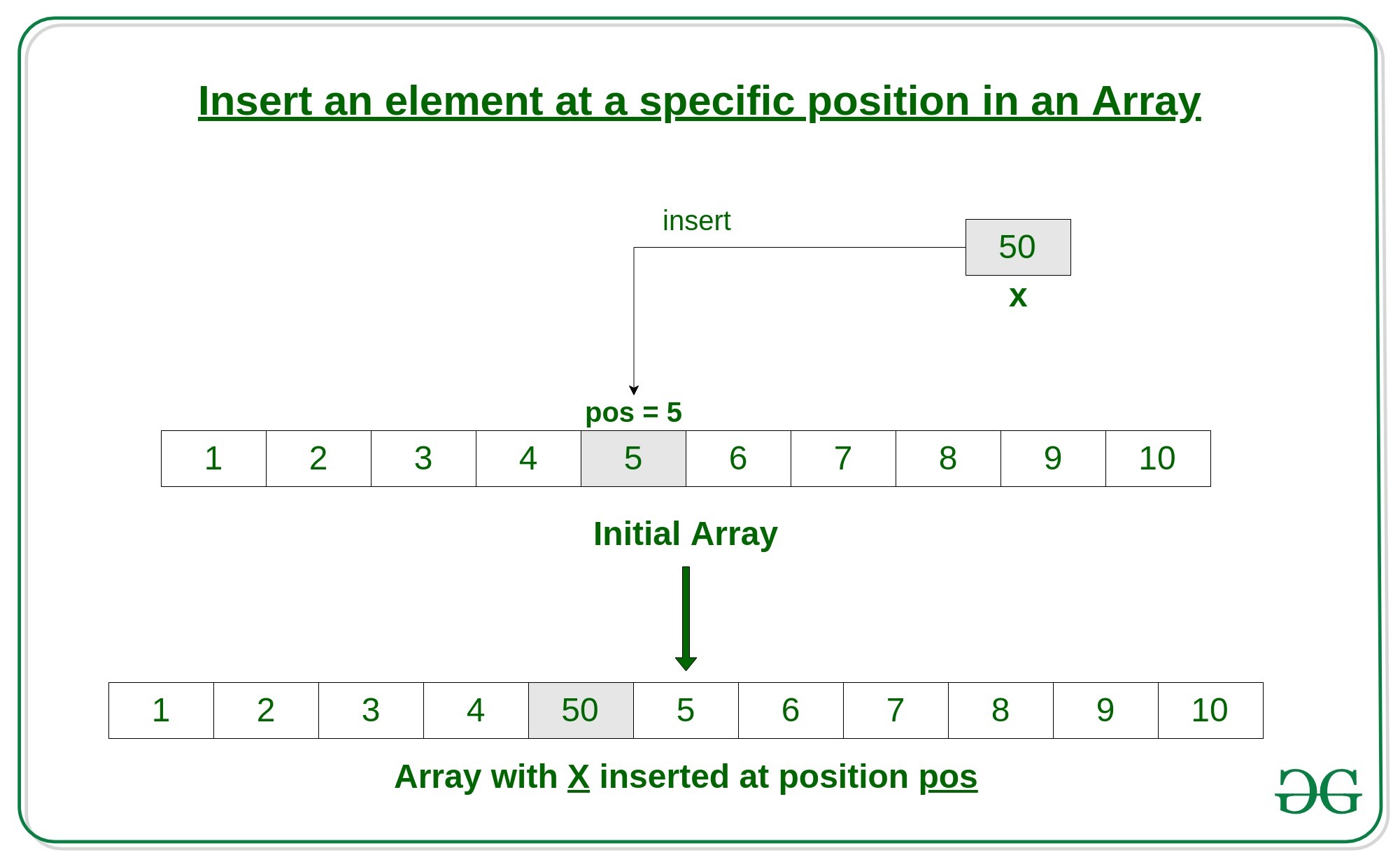
Coding implementation of inserting an element at any position:
// C++ Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to insert element
// at a specific position
void insertElement(int arr[], int n, int x, int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[15] = { 2, 4, 1, 8, 5 };
int n = 5;
cout << "Before insertion : ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
int x = 10, pos = 2;
// Function call
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n++;
cout << "After insertion : ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// C Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to insert element
// at a specific position
void insertElement(int arr[], int n, int x, int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[15] = { 2, 4, 1, 8, 5 };
int n = 5;
printf("Before insertion : ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
int x = 10, pos = 2;
// Function call
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n++;
printf("After insertion : ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
// Java Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
class GFG {
static void insertElement(int arr[], int n, int x,
int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = new int[15];
arr[0] = 2;
arr[1] = 4;
arr[2] = 1;
arr[3] = 8;
arr[4] = 5;
int n = 5;
int x = 10, pos = 2;
System.out.print("Before Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
// Inserting key at specific position
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n += 1;
System.out.print("\n\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by syedsarfarazahammed
# python Program to Insert an element
# at a specific position in an Array
def insertElement(arr, n, x, pos):
# shift elements to the right
# which are on the right side of pos
for i in range(n-1, pos-1, -1):
arr[i + 1] = arr[i]
arr[pos] = x
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Declaring array and key to delete
# here -1 is for empty space
arr = [2, 4, 1, 8, 5, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
n = 5
print("Before insertion : ")
for i in range(0, n):
print(arr[i], end=' ')
print("\n")
x = 10
pos = 2
# Function call
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos)
n += 1
print("After insertion : ")
for i in range(0, n):
print(arr[i], end=' ')
# This Code is contributed by aditya942003patil
// C# program to implement insert
// operation in an unsorted array.
using System;
class main {
static void insertElement(int[] arr, int n, int x,
int pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
for (int i = n - 1; i >= pos; i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[pos] = x;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 2;
arr[1] = 4;
arr[2] = 1;
arr[3] = 8;
arr[4] = 5;
int x = 10;
int n = 5;
int pos = 2;
Console.Write("Before Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
// Inserting key at specific position
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n += 1;
Console.Write("\n\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sourabhdalal0001
// javascript Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
function insertElement(arr, n, x, pos)
{
// shift elements to the right
// which are on the right side of pos
var i = n - 1;
for (i; i >= pos; i--)
{
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
}
arr[pos] = x;
}
var arr = Array(15).fill(0);
arr[0] = 2;
arr[1] = 4;
arr[2] = 1;
arr[3] = 8;
arr[4] = 5;
var n = 5;
var x = 10;
var pos = 2;
console.log("Before Insertion: ");
var i = 0;
for (i; i < n; i++)
{
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Inserting key at specific position
insertElement(arr, n, x, pos);
n += 1;
console.log("\n\nAfter Insertion: ");
i = 0;
for (i; i < n; i++)
{
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
}
// This code is contributed by sourabhdalal0001.
<?php
// Function to insert element at a specific position
function insertElement(&$arr, $n, $x, $pos) {
// shift elements to the right which are on the right side of pos
for ($i = $n - 1; $i >= $pos; $i--) {
$arr[$i + 1] = $arr[$i];
}
// insert the new element at the specified position
$arr[$pos] = $x;
}
// Driver's code
$arr = array(2, 4, 1, 8, 5);
$n = 5;
echo "Before insertion : ";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
}
echo "\n";
$x = 10;
$pos = 2;
// Function call
insertElement($arr, $n, $x, $pos);
$n++;
echo "After insertion : ";
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
}
?>
Output
Before insertion : 2 4 1 8 5 After insertion : 2 4 10 1 8 5
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
3. Inserting Elements in a Sorted Array:
In a sorted array, a search operation is performed for the possible position of the given element by using Binary search, and then an insert operation is performed followed by shifting the elements. And in an unsorted array, the insert operation is faster as compared to the sorted array because we don’t have to care about the position at which the element is placed.
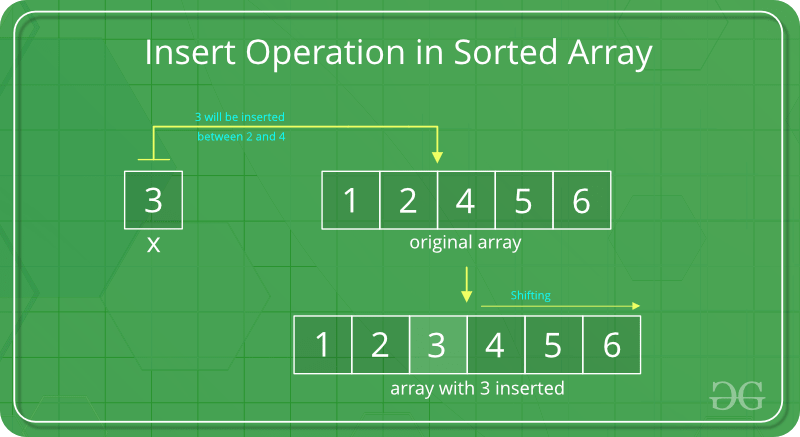
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
// C program to implement insert operation in
// an sorted array.
#include <stdio.h>
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given capacity. n is current
// size of arr[]. This function returns n+1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
int insertSorted(int arr[], int n, int key, int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is already
// more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
int i;
for (i = n - 1; (i >= 0 && arr[i] > key); i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[i + 1] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
int arr[20] = { 12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70 };
int capacity = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
printf("\nBefore Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
// Function call
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
printf("\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
// Java program to insert an
// element in a sorted array
class Main {
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given
// capacity. n is current size of arr[].
// This function returns n+1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
static int insertSorted(int arr[], int n, int key,
int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is already
// more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
int i;
for (i = n - 1; (i >= 0 && arr[i] > key); i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[i + 1] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
/* Driver code */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = new int[20];
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
int capacity = arr.length;
int n = 6;
int key = 26;
System.out.print("\nBefore Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
// Function call
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
System.out.print("\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
# Python3 program to implement insert
# operation in an sorted array.
# Inserts a key in arr[] of given capacity.
# n is current size of arr[]. This function
# returns n+1 if insertion is successful, else n.
def insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity):
# Cannot insert more elements if n is
# already more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity):
return n
i = n - 1
while i >= 0 and arr[i] > key:
arr[i + 1] = arr[i]
i -= 1
arr[i + 1] = key
return (n + 1)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70]
for i in range(20):
arr.append(0)
capacity = len(arr)
n = 6
key = 26
print("Before Insertion: ", end=" ")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
# Function call
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity)
print("\nAfter Insertion: ", end="")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar
using System;
// C# program to insert an
// element in a sorted array
public class GFG {
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given
// capacity. n is current size of arr[].
// This function returns n+1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
public static int insertSorted(int[] arr, int n,
int key, int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is already
// more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity) {
return n;
}
int i;
for (i = n - 1; (i >= 0 && arr[i] > key); i--) {
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
}
arr[i + 1] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
/* Driver code */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[20];
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
int capacity = arr.Length;
int n = 6;
int key = 26;
Console.Write("\nBefore Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Function call
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
Console.Write("\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
// JavaScript program to insert an
// element in a sorted array
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given
// capacity. n is current size of arr[].
// This function returns n+1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
function insertSorted( arr, n, key, capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is already
// more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
var i;
for (i = n - 1; (i >= 0 && arr[i] > key); i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[i + 1] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
var arr = new Array(20);
arr[0] = 12;
arr[1] = 16;
arr[2] = 20;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
arr[5] = 70;
var capacity = arr.length;
var n = 6;
var key = 26;
document.write("\nBefore Insertion: ");
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
// Inserting key
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
document.write("<br>" +"\nAfter Insertion: ");
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
console.log(arr[i] + " ");
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
// C++ program to implement insert operation in
// an sorted array.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Inserts a key in arr[] of given capacity. n is current
// size of arr[]. This function returns n+1 if insertion
// is successful, else n.
int insertSorted(int arr[], int n, int key, int capacity)
{
// Cannot insert more elements if n is already
// more than or equal to capacity
if (n >= capacity)
return n;
int i;
for (i = n - 1; (i >= 0 && arr[i] > key); i--)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
arr[i + 1] = key;
return (n + 1);
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
int arr[20] = { 12, 16, 20, 40, 50, 70 };
int capacity = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int n = 6;
int i, key = 26;
cout << "\nBefore Insertion: ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
// Function call
n = insertSorted(arr, n, key, capacity);
cout << "\nAfter Insertion: ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10
Output
Before Insertion: 12 16 20 40 50 70 After Insertion: 12 16 20 26 40 50 70
Time Complexity: O(N) [In the worst case all elements may have to be moved]
Auxiliary Space: O(1)