Taking input in Python
Last Updated :
21 Dec, 2023
Developers often have a need to interact with users, either to get data or to provide some sort of result. Most programs today use a dialog box as a way of asking the user to provide some type of input. While Python provides us with two inbuilt functions to read the input from the keyboard.
- input ( prompt )
- raw_input ( prompt )
input (): This function first takes the input from the user and converts it into a string. The type of the returned object always will be <class ‘str’>. It does not evaluate the expression it just returns the complete statement as String. For example, Python provides a built-in function called input which takes the input from the user. When the input function is called it stops the program and waits for the user’s input. When the user presses enter, the program resumes and returns what the user typed.
Syntax:
inp = input('STATEMENT')
Example:
1. >>> name = input('What is your name?\n') # \n ---> newline ---> It causes a line break
>>> What is your name?
Ram
>>> print(name)
Ram
# ---> comment in python
Python3
val = input("Enter your value: ")
print(val)
|
Output:

Taking String as an input:
Python3
name = input('What is your name?\n')
print(name)
|
Output:
What is your name?
Ram
Ram
How the input function works in Python :
- When input() function executes program flow will be stopped until the user has given input.
- The text or message displayed on the output screen to ask a user to enter an input value is optional i.e. the prompt, which will be printed on the screen is optional.
- Whatever you enter as input, the input function converts it into a string. if you enter an integer value still input() function converts it into a string. You need to explicitly convert it into an integer in your code using typecasting.
Code:
Python3
num = input ("Enter number :")
print(num)
name1 = input("Enter name : ")
print(name1)
print ("type of number", type(num))
print ("type of name", type(name1))
|
Output:

raw_input(): This function works in older version (like Python 2.x). This function takes exactly what is typed from the keyboard, converts it to string, and then returns it to the variable in which we want to store it.
Example:
Python
g = raw_input("Enter your name : ")
print g
|
Output:
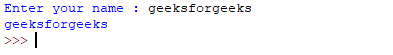
Here, g is a variable that will get the string value, typed by the user during the execution of the program. Typing of data for the raw_input() function is terminated by enter key. We can use raw_input() to enter numeric data also. In that case, we use typecasting. For more details on typecasting refer this.
Note: input() function takes all the input as a string only
There are various function that are used to take as desired input few of them are : –
- int(input())
- float(input())
Python3
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(num, " ", type(num))
floatNum = float(input("Enter a decimal number: "))
print(floatNum, " ", type(floatNum))
|
Output:
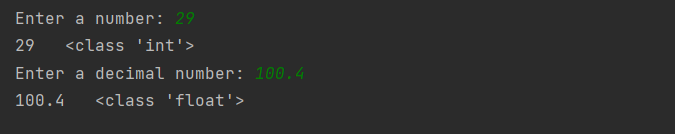
Output
Refer to the article Taking list as input from the user for more information.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...