Insertion in a Doubly Linked List
Last Updated :
18 Mar, 2024
Inserting a new node in a doubly linked list is very similar to inserting new node in linked list. There is a little extra work required to maintain the link of the previous node. A node can be inserted in a Doubly Linked List in four ways:
- At the front of the DLL.
- In between two nodes
- After a given node.
- Before a given node.
- At the end of the DLL.
Insertion at the Beginning in Doubly Linked List:
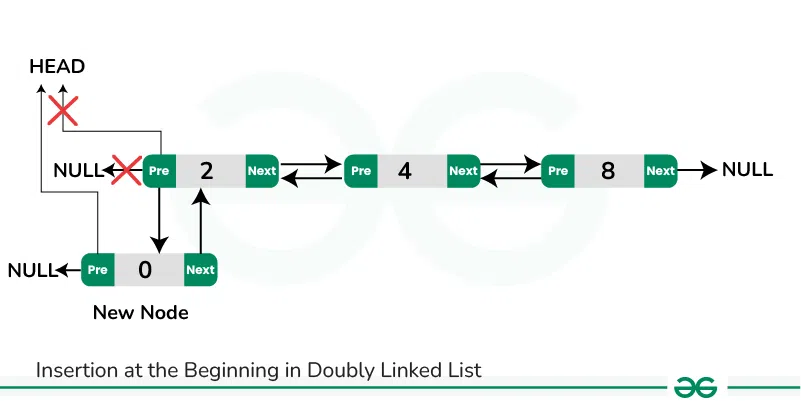
To insert a new node at the beginning of the doubly list, we can use the following steps:
- Allocate memory for a new node (say new_node) and assign the provided value to its data field.
- Set the previous pointer of the new_node to nullptr.
- If the list is empty:
- Set the next pointer of the new_node to nullptr.
- Update the head pointer to point to the new_node.
- If the list is not empty:
- Set the next pointer of the new_node to the current head.
- Update the previous pointer of the current head to point to the new_node.
- Update the head pointer to point to the new_node.
Below is the implementation of the 5 steps to insert a node at the front of the linked list:
C++
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
// of a list and an int, inserts a new node
// on the front of the list.
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
// and previous as NULL
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
// of a list and an int, inserts a new node
// on the front of the list.
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data */
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
// Adding a node at the front of the list
function push(new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
let new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
// This code is contributed by saurabh_jaiswal.
# Adding a node at the front of the list
def push(self, new_data):
# 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data
new_node = Node(data=new_data)
# 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL
new_node.next = self.head
new_node.prev = None
# 4. change prev of head node to new node
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
# 5. move the head to point to the new node
self.head = new_node
# This code is contributed by jatinreaper
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Insertion in between two nodes in Doubly Linked List:
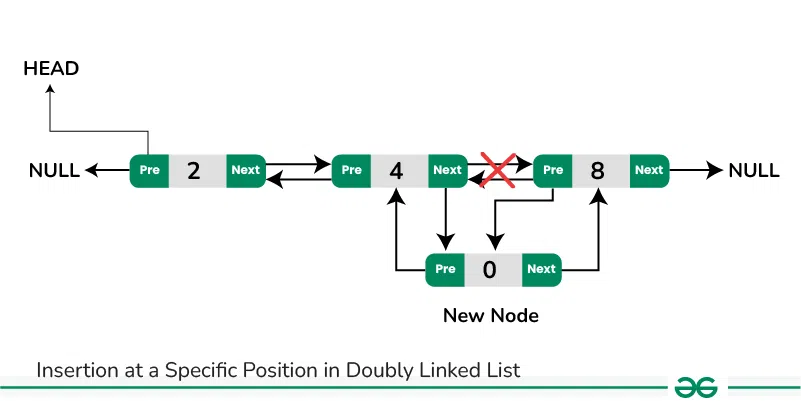
1. Add a node after a given node in a Doubly Linked List:
We are given a pointer to a node as prev_node, and the new node is inserted after the given node. This can be done using the following steps:
- Firstly create a new node (say new_node).
- Now insert the data in the new node.
- Point the next of new_node to the next of prev_node.
- Point the next of prev_node to new_node.
- Point the previous of new_node to prev_node.
- Point the previous of next of new_node to new_node.
Below is the implementation of the steps to insert a node after a given node in the linked list:
C++
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "the given previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
// 1. allocate new node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node->prev = prev_node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node->next != NULL)
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL) {
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 1. allocate new node
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node->prev = prev_node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node->next != NULL)
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
public void InsertAfter(Node prev_Node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_Node == null) {
System.out.println(
"The given previous node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_Node.next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
public void InsertAfter(Node prev_Node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_Node == null) {
Console.WriteLine(
"The given previous node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_Node.next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
<script>
function InsertAfter(prev_Node,new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_Node == null) {
document.write("The given previous node cannot be NULL <br>");
return;
}
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
let new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_Node.next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
# Given a node as prev_node, insert
# a new node after the given node
def insertAfter(self, prev_node, new_data):
# Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if prev_node is None:
print("This node doesn't exist in DLL")
return
# 1. allocate node &
# 2. put in the data
new_node = Node(data=new_data)
# 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_node.next
# 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_node.next = new_node
# 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node.prev = prev_node
# 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if new_node.next is not None:
new_node.next.prev = new_node
# This code is contributed by jatinreaper
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
2. Add a node before a given node in a Doubly Linked List:
Let the pointer to this given node be next_node. This can be done using the following steps.
- Allocate memory for the new node, let it be called new_node.
- Put the data in new_node.
- Set the previous pointer of this new_node as the previous node of the next_node.
- Set the previous pointer of the next_node as the new_node.
- Set the next pointer of this new_node as the next_node.
- Set the next pointer of the previous of new_node to new_node.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
void insertBefore(Node* next_node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_node is NULL
if (next_node == NULL) {
printf("the given next node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate new node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of next_node
new_node->prev = next_node->prev;
// 4. Make the previous of next_node as new_node
next_node->prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node->next = next_node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node->prev != NULL)
new_node->prev->next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
void insertBefore(struct Node* next_node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_node is NULL
if (next_node == NULL) {
printf("the given next node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate new node
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of next_node
new_node->prev = next_node->prev;
// 4. Make the previous of next_node as new_node
next_node->prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node->next = next_node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node->prev != NULL)
new_node->prev->next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
public void InsertBefore(Node next_Node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_node is NULL
if (next_Node == null) {
System.out.println(
"The given next node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate node
// 2. Put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of prev_node
new_node.prev = next_Node.prev;
// 4. Make the prev of next_node as new_node
next_Node.prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node.next = next_Node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node.prev != null)
new_node.prev.next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
public void InsertAfter(Node next_Node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_node is NULL
if (next_Node == null) {
Console.WriteLine(
"The given next node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate node
// 2. Put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of next_node
new_node.prev = next_Node.prev;
// 4. Make the previous of next_node as new_node
next_Node.prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node.next = next_Node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node.prev != null)
new_node.prev.next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
<script>
function InsertAfter(next_Node,new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_Node is NULL
if (next_Node == null) {
document.write("The given next node cannot be NULL <br>");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate node
// 2. Put in the data
let new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of next_node
new_node.prev = next_Node.prev;
// 4. Make the previous of next_node as new_node
next_Node.prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node.next = next_Node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node.prev != null)
new_node.prev.next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
# Given a node as prev_node, insert
# a new node after the given node
def insertAfter(self, next_node, new_data):
# Check if the given next_node is NULL
if next_node is None:
print("This node doesn't exist in DLL")
return
# 1. Allocate node &
# 2. Put in the data
new_node = Node(data=new_data)
# 3. Make previous of new node as previous of prev_node
new_node.prev = next_node.prev
# 4. Make the previous of next_node as new_node
next_node.prev = new_node
# 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node.next = next_node
# 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if new_node.prev is not None:
new_node.prev.next = new_node
else:
head = new_node
# This code is contributed by jatinreaper
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Insertion at the End in Doubly Linked List:
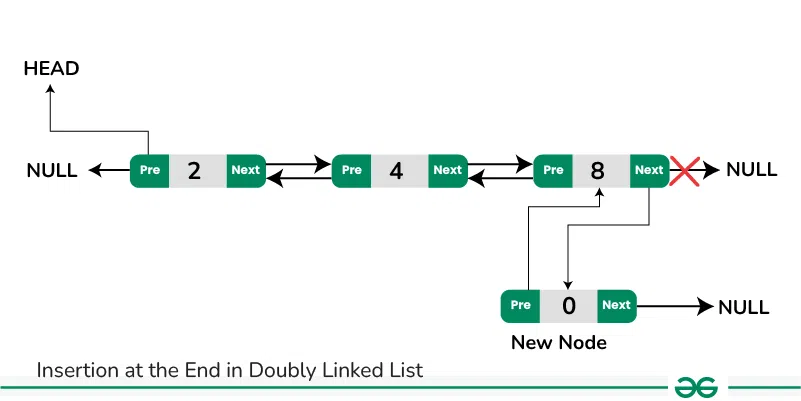
The new node is always added after the last node of the given Linked List. This can be done using the following steps:
- Create a new node (say new_node).
- Put the value in the new node.
- Make the next pointer of new_node as null.
- If the list is empty, make new_node as the head.
- Otherwise, travel to the end of the linked list.
- Now make the next pointer of last node point to new_node.
- Change the previous pointer of new_node to the last node of the list.
Below is the implementation of the steps to insert a node at the end of the linked list:
C++
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
// of a DLL and an int, appends a new node at the end
void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
Node* last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so
// make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new
// node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
new_node->prev = NULL;
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
// 7. Make last node as previous of new node
new_node->prev = last;
return;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
// of a DLL and an int, appends a new node at the end
void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node* last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so
// make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new
// node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
new_node->prev = NULL;
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
// 7. Make last node as previous of new node
new_node->prev = last;
return;
}
// Add a node at the end of the list
void append(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
Node last = head; /* used in step 5*/
// 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so
// make next of it as NULL
new_node.next = null;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new
// node as head
if (head == null) {
new_node.prev = null;
head = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last.next = new_node;
// 7. Make last node as previous of new node
new_node.prev = last;
}
// Add a node at the end of the list
void append(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
Node last = head; /* used in step 5*/
// 3. This new node is going
// to be the last node, so
// make next of it as NULL
new_node.next = null;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (head == null) {
new_node.prev = null;
head = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last.next = new_node;
// 7. Make last node as previous of new node
new_node.prev = last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
<script>
// Add a node at the end of the list
function append(new_data)
{
/* 1. allocate node
* 2. put in the data */
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
var last = head; /* used in step 5*/
/* 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so
* make next of it as NULL*/
new_node.next = null;
/* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new
* node as head */
if (head == null) {
new_node.prev = null;
head = new_node;
return;
}
/* 5. Else traverse till the last node */
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
/* 6. Change the next of last node */
last.next = new_node;
/* 7. Make last node as previous of new node */
new_node.prev = last;
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
# Add a node at the end of the DLL
def append(self, new_data):
# 1. allocate node
# 2. put in the data
new_node = Node(data=new_data)
last = self.head
# 3. This new node is going to be the
# last node, so make next of it as NULL
new_node.next = None
# 4. If the Linked List is empty, then
# make the new node as head
if self.head is None:
new_node.prev = None
self.head = new_node
return
# 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last.next is not None):
last = last.next
# 6. Change the next of last node
last.next = new_node
# 7. Make last node as previous of new node */
new_node.prev = last
# This code is contributed by jatinreaper
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Related Articles:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...