Insertion in Linked List
Last Updated :
22 Feb, 2024
Given a Linked List, the task is to insert a new node in this given Linked List at the following positions:
- At the front of the linked list
- After a given node.
- At the end of the linked list.
Approach:
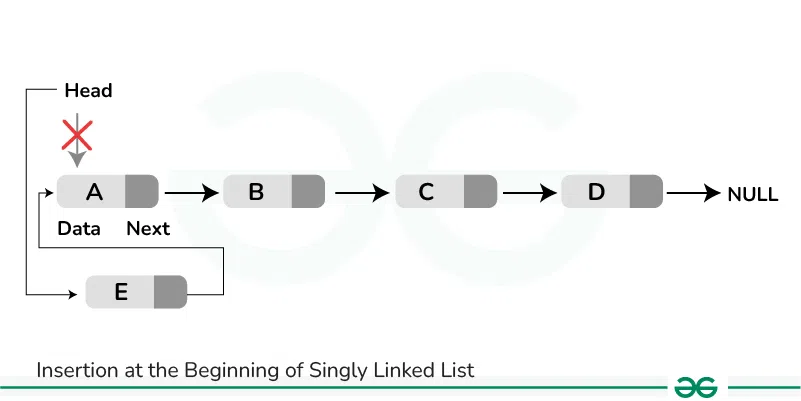
To insert a node at the start/beginning/front of a Linked List, we need to:
- Make the first node of Linked List linked to the new node
- Remove the head from the original first node of Linked List
- Make the new node as the Head of the Linked List.
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
|
C
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
|
Java
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
|
Python3
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
|
C#
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function push(new_data)
{
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(1), We have a pointer to the head and we can directly attach a node and change the pointer. So the Time complexity of inserting a node at the head position is O(1) as it does a constant amount of work.
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Refer this post for detailed implementation of the above approach.
Approach:
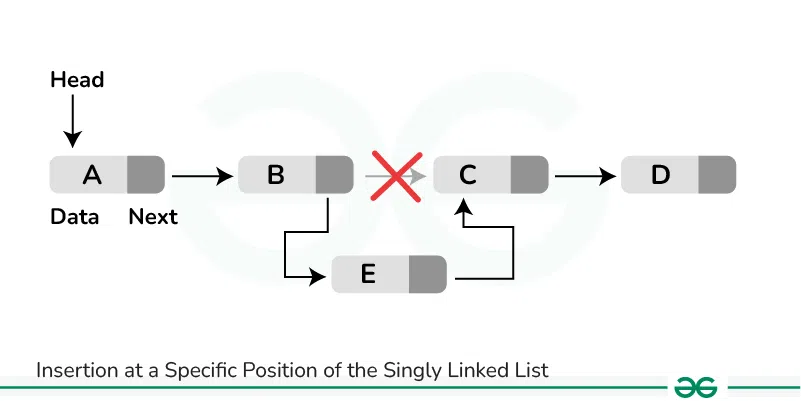
To insert a node after a given node in a Linked List, we need to:
- Check if the given node exists or not.
- If it do not exists,
- If the given node exists,
- Make the element to be inserted as a new node
- Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
- Now shift the original next pointer of given node to the next pointer of new node
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "The given previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
|
C
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
if (prev_node == NULL) {
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
|
Java
public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data)
{
if (prev_node == null) {
System.out.println(
"The given previous node cannot be null");
return;
}
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
prev_node.next = new_node;
}
|
Python3
def insertAfter(self, prev_node, new_data):
if prev_node is None:
print("The given previous node must inLinkedList.")
return
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = prev_node.next
prev_node.next = new_node
|
C#
public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data)
{
if (prev_node == null) {
Console.WriteLine("The given previous node"
+ " cannot be null");
return;
}
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
prev_node.next = new_node;
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function insertAfter(prev_node, new_data)
{
if (prev_node == null)
{
document.write("The given previous node cannot be null");
return;
}
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
prev_node.next = new_node;
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time complexity: O(1), since prev_node is already given as argument in a method, no need to iterate over list to find prev_node
- Auxiliary Space: O(1) since using constant space to modify pointers
Refer this post for detailed implementation of the above approach.
Approach:
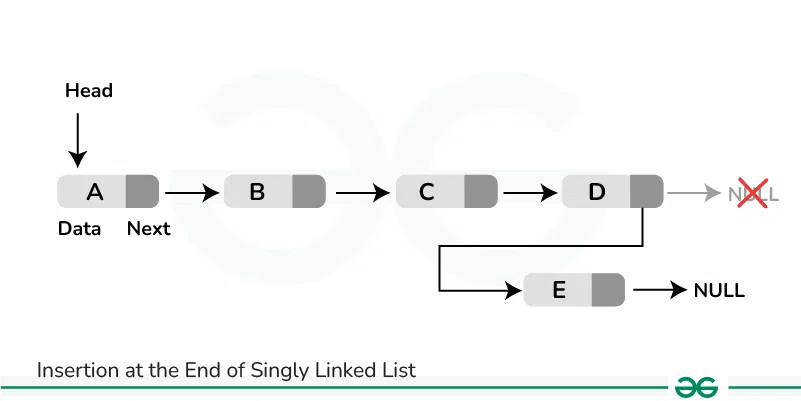
To insert a node at the end of a Linked List, we need to:
- Go to the last node of the Linked List
- Change the next pointer of last node from NULL to the new node
- Make the next pointer of new node as NULL to show the end of Linked List
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
Node* last = *head_ref;
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
while (last->next != NULL) {
last = last->next;
}
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
|
C
void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node* last = *head_ref;
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
|
Java
public void append(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
new_node.next = null;
Node last = head;
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
last.next = new_node;
return;
}
|
Python3
def append(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
last = self.head
while (last.next):
last = last.next
last.next = new_node
|
C#
public void append(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
new_node.next = null;
Node last = head;
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
last.next = new_node;
return;
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function append(new_data)
{
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null)
{
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
new_node.next = null;
var last = head;
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
last.next = new_node;
return;
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the linked list. Since there is a loop from head to end, the function does O(n) work.
- This method can also be optimized to work in O(1) by keeping an extra pointer to the tail of the linked list/
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Refer this post for detailed implementation of the above approach.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...