Delete a node in a Doubly Linked List
Last Updated :
10 Jan, 2023
Write a function to delete a given node in a doubly-linked list.
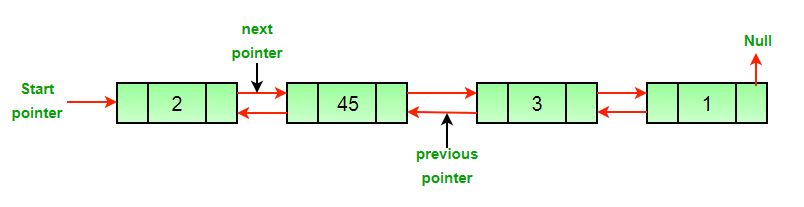
Example:
Input: DLL = 2->45->3->1, Node = 45
Output: 2->3->1
Input: DLL = 2->45->3->1, Node = 1
Output: 2->45->3
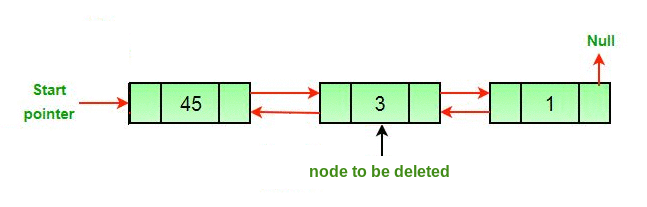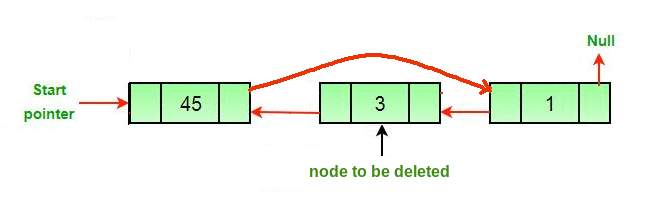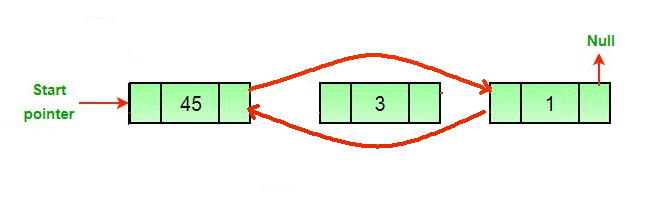
Approach: The deletion of a node in a doubly-linked list can be divided into three main categories:
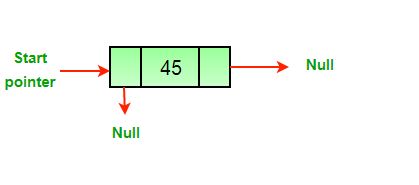
- After the deletion of the head node.
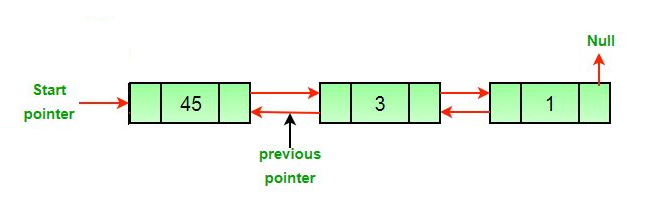
- After the deletion of the middle node.
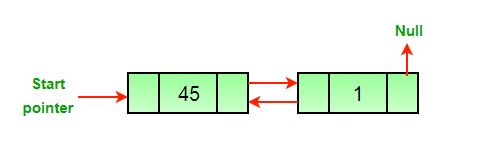
- After the deletion of the last node.
All three mentioned cases can be handled in two steps if the pointer of the node to be deleted and the head pointer is known.
- If the node to be deleted is the head node then make the next node as head.
- If a node is deleted, connect the next and previous node of the deleted node.
Algorithm:
- Let the node to be deleted be del.
- If node to be deleted is head node, then change the head pointer to next current head.
if headnode == del then
headnode = del.nextNode
- Set prev of next to del, if next to del exists.
if del.nextNode != none
del.nextNode.previousNode = del.previousNode
- Set next of previous to del, if previous to del exists.
if del.previousNode != none
del.previousNode.nextNode = del.next
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
};
void deleteNode(Node** head_ref, Node* del)
{
if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL)
return;
if (*head_ref == del)
*head_ref = del->next;
if (del->next != NULL)
del->next->prev = del->prev;
if (del->prev != NULL)
del->prev->next = del->next;
free(del);
return;
}
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->prev = NULL;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
cout << "Original Linked list ";
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, head);
deleteNode(&head, head->next);
deleteNode(&head, head->next);
cout << "\nModified Linked list ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
void deleteNode(struct Node** head_ref, struct Node* del)
{
if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL)
return;
if (*head_ref == del)
*head_ref = del->next;
if (del->next != NULL)
del->next->prev = del->prev;
if (del->prev != NULL)
del->prev->next = del->next;
free(del);
return;
}
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->prev = NULL;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
printf("\n Original Linked list ");
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, head);
deleteNode(&head, head->next);
deleteNode(&head, head->next);
printf("\n Modified Linked list ");
printList(head);
getchar();
}
|
Java
public class DLL {
Node head;
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
head = new_Node;
}
public void printlist(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
void deleteNode(Node del)
{
if (head == null || del == null) {
return;
}
if (head == del) {
head = del.next;
}
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
if (del.prev != null) {
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
return;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DLL dll = new DLL();
dll.push(2);
dll.push(4);
dll.push(8);
dll.push(10);
System.out.print("Original Linked list ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next);
System.out.print(
"\nModified Linked list ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
}
}
|
Python3
import gc
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def deleteNode(self, dele):
if self.head is None or dele is None:
return
if self.head == dele:
self.head = dele.next
if dele.next is not None:
dele.next.prev = dele.prev
if dele.prev is not None:
dele.prev.next = dele.next
gc.collect()
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
def printList(self, node):
while(node is not None):
print(node.data,end=' ')
node = node.next
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.push(2);
dll.push(4);
dll.push(8);
dll.push(10);
print ("\n Original Linked List",end=' ')
dll.printList(dll.head)
dll.deleteNode(dll.head)
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next)
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next)
print("\n Modified Linked List",end=' ')
dll.printList(dll.head)
|
C#
using System;
public class DLL
{
Node head;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
head = new_Node;
}
public void printlist(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
void deleteNode(Node del)
{
if (head == null || del == null)
{
return;
}
if (head == del)
{
head = del.next;
}
if (del.next != null)
{
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
if (del.prev != null)
{
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
return;
}
public static void Main()
{
DLL dll = new DLL();
dll.push(2);
dll.push(4);
dll.push(8);
dll.push(10);
Console.Write("Original Linked list ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next);
Console.Write("Modified Linked list ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
function push(new_data) {
new_Node = new Node(new_data);
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
head = new_Node;
}
function printlist( node) {
last = null;
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
document.write("<br/>");
}
function deleteNode( del) {
if (head == null || del == null) {
return;
}
if (head == del) {
head = del.next;
}
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
if (del.prev != null) {
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
return;
}
push(2);
push(4);
push(8);
push(10);
document.write("Created DLL is: ");
printlist(head);
deleteNode(head);
deleteNode(head.next);
deleteNode(head.next);
document.write("Modified Linked list: ");
printlist(head);
</script>
|
Output
Original Linked list 10 8 4 2
Modified Linked list 8
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(1).
Since traversal of the linked list is not required so the time complexity is constant.
- Auxiliary Space: O(1).
As no extra space is required, so the space complexity is constant.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...